Data Source Node
The Data Source Node provides static input for your workflow. You can supply text, Markdown, JSON data, or attach local files (including images and code) directly as input for downstream nodes.
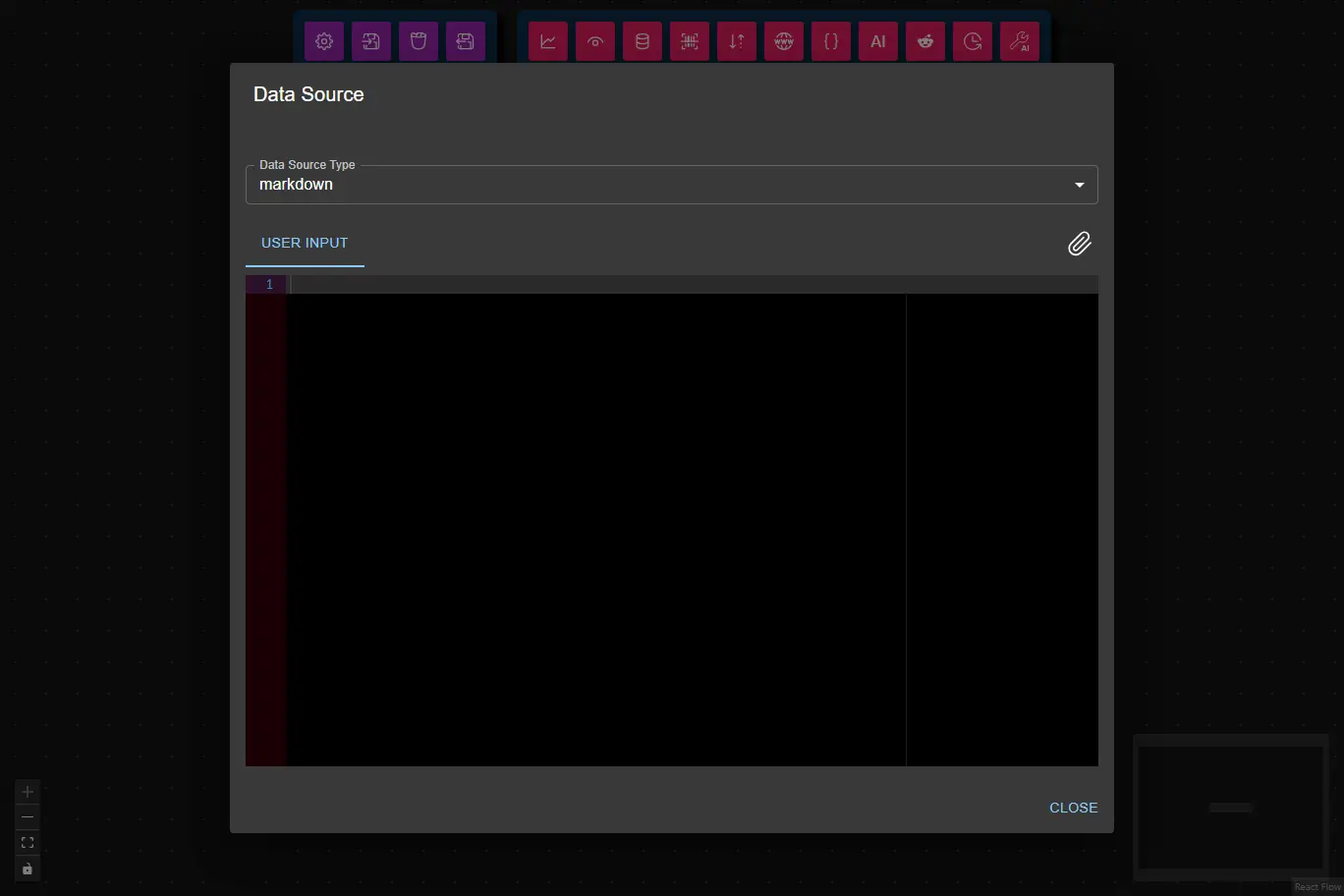
Configuration
- Markdown
- Json
For Markdown: Enter text and optionally attach files.
Note: Currently supported file extensions are .txt, .md, .html, .css, .scss, .js, .ts, .tsx, .json, .xml, .csv, .yaml, .yml, .ini, .log, .sh, .sql, .py, .java, .c, .cpp, .h, .bat, .env, .png, .jpg, .jpeg, .gif, .bmp, .webp, .svg).
Attached files are available to downstream nodes as Markdown code blocks or embedded images.
For JSON: Enter structured JSON data to be passed to downstream nodes.
Example Usage
See the Weather Dashboard workflow, Google Drive Listing workflow or Customer Total Spend Analysis workflow for examples using prompts, configuration, and file attachments.
Common Use Cases
- Prompt Input: Provide instructions or questions for LLM nodes.
- Static Data: Supply sample data for testing or demonstration.
- Configuration: Pass configuration objects to downstream nodes.
- Markdown Content & Files: Input Markdown-formatted text and attach images or code files for rendering or processing.
- JSON Input: Provide structured data for validation, transformation, or visualization.
Best Practices
- Choose the correct type: Use
jsonfor structured data,markdownfor text, rich formatting, or file attachments. - Validate JSON: Ensure your JSON is valid to avoid downstream errors.
- Use Markdown: For rich text and file attachments, use Markdown mode.
- Keep it simple: Use Data Source nodes for static or rarely-changing inputs.
- Attach files as needed: Images and code files can be previewed and used by downstream nodes.
Troubleshooting
Common Issues
- Invalid JSON: If using
jsontype, ensure the value is valid JSON. - Unexpected output: Double-check the data type, value, and attached files.
- Downstream errors: Errors in downstream nodes may be caused by incorrect or missing input.
Performance Tips
- Use for small to medium-sized static data and attachments.
- Use bigger LLM nodes for large data processing tasks.