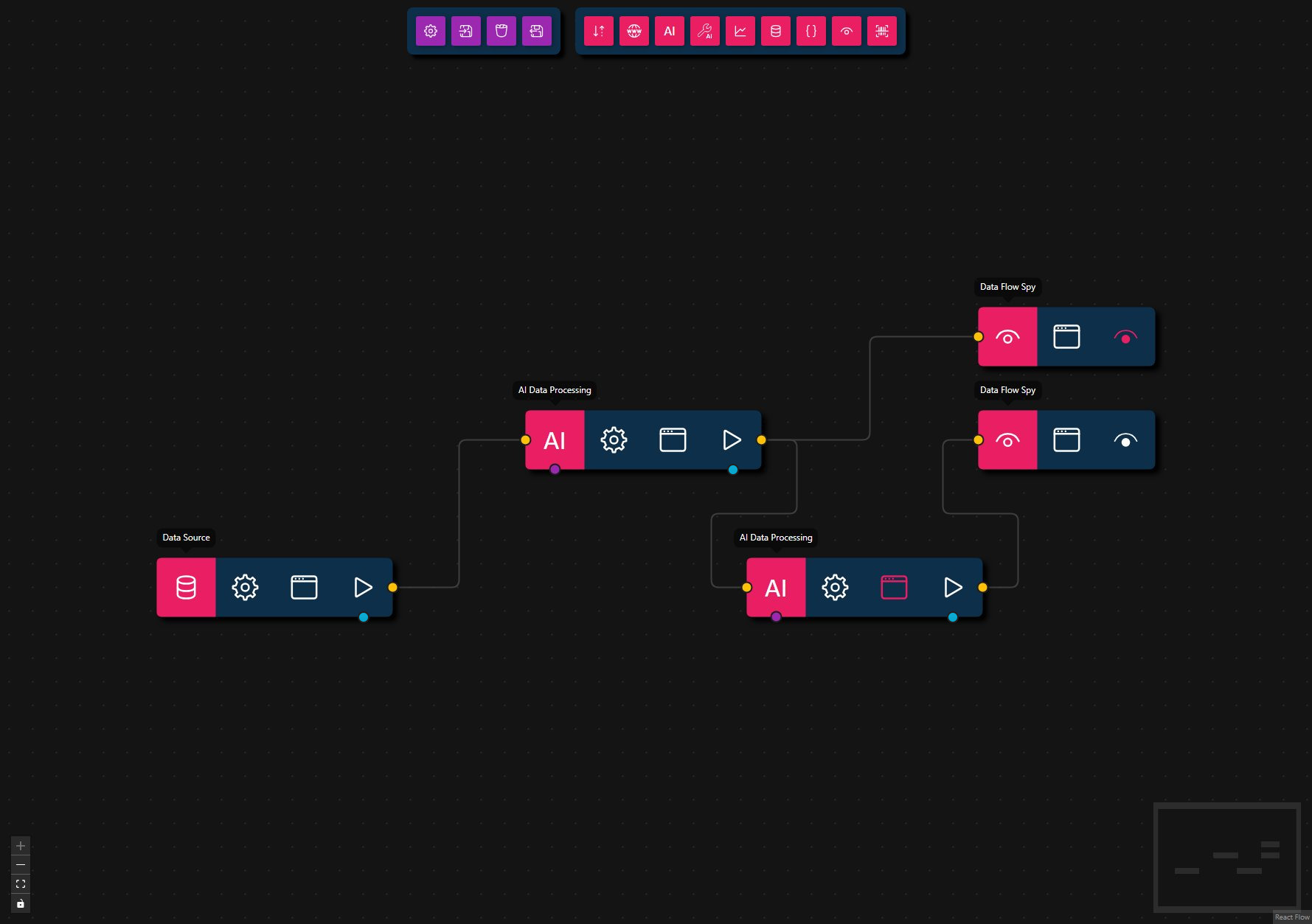
AI Data Processing Overseer Workflow
This workflow demonstrates how to chain multiple AI Data Processing nodes with an overseer node that validates output and triggers a feedback loop for correction.
- Preview
- JSON
- Node Configuration
{
"nodes": [
{
"id": "1f718672-ced2-492d-925a-933c02a3f4a1",
"type": "data-source",
"position": {
"x": 300,
"y": 100
},
"data": {
"title": "Data Source",
"dataSource": {
"value": {
"text": "This is incomplete data.",
"files": []
},
"type": "markdown"
}
},
"measured": {
"width": 160,
"height": 40
},
"selected": false,
"dragging": false
},
{
"id": "e40a9b65-dc2b-41e8-a1e5-88bb365d2ffe",
"type": "llm-process",
"position": {
"x": 550,
"y": 0
},
"data": {
"title": "AI Data Processing",
"prompt": "Summarize the input data. Output a summary as plain text.",
"model": "",
"maxFeedbackLoops": 2
},
"measured": {
"width": 160,
"height": 40
},
"selected": false,
"dragging": false
},
{
"id": "02613504-6c72-4ef1-b638-ff57a4eaff1a",
"type": "llm-process",
"position": {
"x": 700,
"y": 100
},
"data": {
"title": "AI Data Processing",
"prompt": "If the input is not a valid summary respond with an error.",
"model": "",
"maxFeedbackLoops": 0,
"format": {
"onSuccess": "{\r\n \"type\": \"object\",\r\n \"properties\": {\r\n \"output\": { \"type\": \"string\" }\r\n },\r\n \"required\": [\"output\"]\r\n}\r\n",
"onError": "{\r\n \"type\": \"object\",\r\n \"properties\": {\r\n \"error\": { \"type\": \"string\" }\r\n },\r\n \"required\": [\"error\"]\r\n}"
}
},
"measured": {
"width": 160,
"height": 40
},
"selected": true,
"dragging": false
},
{
"id": "d5c8c0c5-21c6-436e-8ee8-362704927af9",
"type": "data-flow-spy",
"position": {
"x": 857,
"y": 0
},
"data": {
"title": "Data Flow Spy"
},
"measured": {
"width": 120,
"height": 40
},
"selected": false,
"dragging": false
},
{
"id": "799eba41-c42d-47af-9d4e-bb6a52efba29",
"type": "data-flow-spy",
"position": {
"x": 857,
"y": -70
},
"data": {
"title": "Data Flow Spy"
},
"measured": {
"width": 120,
"height": 40
},
"selected": false,
"dragging": false
}
],
"edges": [
{
"type": "smoothstep",
"animated": false,
"source": "1f718672-ced2-492d-925a-933c02a3f4a1",
"sourceHandle": "right-source",
"target": "e40a9b65-dc2b-41e8-a1e5-88bb365d2ffe",
"targetHandle": "left-target",
"id": "xy-edge__1f718672-ced2-492d-925a-933c02a3f4a1right-source-e40a9b65-dc2b-41e8-a1e5-88bb365d2ffeleft-target"
},
{
"type": "smoothstep",
"animated": false,
"source": "e40a9b65-dc2b-41e8-a1e5-88bb365d2ffe",
"sourceHandle": "right-source",
"target": "02613504-6c72-4ef1-b638-ff57a4eaff1a",
"targetHandle": "left-target",
"id": "xy-edge__e40a9b65-dc2b-41e8-a1e5-88bb365d2fferight-source-02613504-6c72-4ef1-b638-ff57a4eaff1aleft-target"
},
{
"type": "smoothstep",
"animated": false,
"source": "02613504-6c72-4ef1-b638-ff57a4eaff1a",
"sourceHandle": "right-source",
"target": "d5c8c0c5-21c6-436e-8ee8-362704927af9",
"targetHandle": "left-target",
"id": "xy-edge__02613504-6c72-4ef1-b638-ff57a4eaff1aright-source-d5c8c0c5-21c6-436e-8ee8-362704927af9left-target"
},
{
"type": "smoothstep",
"animated": false,
"source": "e40a9b65-dc2b-41e8-a1e5-88bb365d2ffe",
"sourceHandle": "right-source",
"target": "799eba41-c42d-47af-9d4e-bb6a52efba29",
"targetHandle": "left-target",
"id": "xy-edge__e40a9b65-dc2b-41e8-a1e5-88bb365d2fferight-source-799eba41-c42d-47af-9d4e-bb6a52efba29left-target"
}
]
}
- Data Source
- Input:
"This is incomplete data."
- Input:
- AI Data Processing (Worker)
- Prompt: Summarize the input data. Output a summary as plain text.
- Model: llama3.1:8b
- Max Feedback Loops: 2
- AI Data Processing (Overseer)
- Prompt: If the input is not a valid summary, respond with an error.
- Model: llama3.1:8b
- Max Feedback Loops: 0
- Structured Output:
- On Success:
{ "output": string } - On Error:
{ "error": string }
- On Success:
- Data Flow Spy (Worker)
- Output: Displays the worker AI Data Processing node result.
- Data Flow Spy (Overseer)
- Output: will not display a response since the overseer AI Data Processing node will not return a response while there is an error.
Steps
- Provide Input: The workflow starts with a Data Source node that supplies incomplete data.
- Summarize: The first AI Data Processing node attempts to summarize the input as plain text.
- Oversee & Validate: The overseer AI Data Processing node (second one in the workflow) receives the summary and determines if it is valid. If the input is not a valid summary, it sends back the error to the previous node.
- Feedback Loop: If an error is detected, the feedback loop triggers the first AI Data Processing node to retry, correcting its output.
- Inspect Output: The Data Flow Spy nodes display the final results for both AI Data Processing nodes (the overseer AI Data Processing node will not return a response while there is an error).
Common Use Cases
- Automated Output Correction: Ensure AI-generated outputs meet strict format requirements.
- Chained AI Validation: Use an overseer node to validate and enforce output schemas.
- Error Feedback Loops: Automatically retry and correct outputs until they meet validation criteria.
Best Practices
- Define clear success and error schemas in the overseer node.
- Use feedback loops to improve output reliability.
- Inspect intermediate results with Data Flow Spy nodes for easier debugging.
Troubleshooting
- Infinite Loops: Set a reasonable max feedback loop count to avoid endless retries.
- Model Limitations: Some models may not reliably follow structured output instructions.
- Schema Mismatch: Ensure your overseer node's schemas match the expected output format.